A microservices architecture means more requests on the network, and more opportunities for malicious parties to intercept traffic. Mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication is a way to encrypt services traffic using certificates.
With Istio, you can enforce mutual TLS automatically, outside of your application code, with a single YAML file. This works because the Istio control plane mounts client certificates into the sidecar proxies for you, so that pods can authenticate with each other.
Let’s enable mutual TLS for the entire service mesh, including the two services (client and server) pictured below.
Starting in Istio 1.5, Istio uses automatic mutual TLS. This means that while services accept both plain-text and TLS traffic, by default, services will send TLS requests within the cluster. This means that the client-to-server above will already be encrypted with the default Istio install. (But HTTP will still work.)
We can test this by sending a plain HTTP request from the client pod’s Istio proxy container to the server. The request succeeds:
$ curl http://server:80
Hello World! /$
To enforce mTLS such that only TLS traffic is accepted by all services in all Istio-injected namespacess, we’ll apply the following Istio PeerAuthentication resource:
apiVersion: "security.istio.io/v1beta1"
kind: "PeerAuthentication"
metadata:
name: "default"
namespace: "istio-system"
spec:
mtls:
mode: STRICT
Now let’s try to send another request between client and server:
$ curl http://server:80
curl: (56) Recv failure: Connection reset by peer
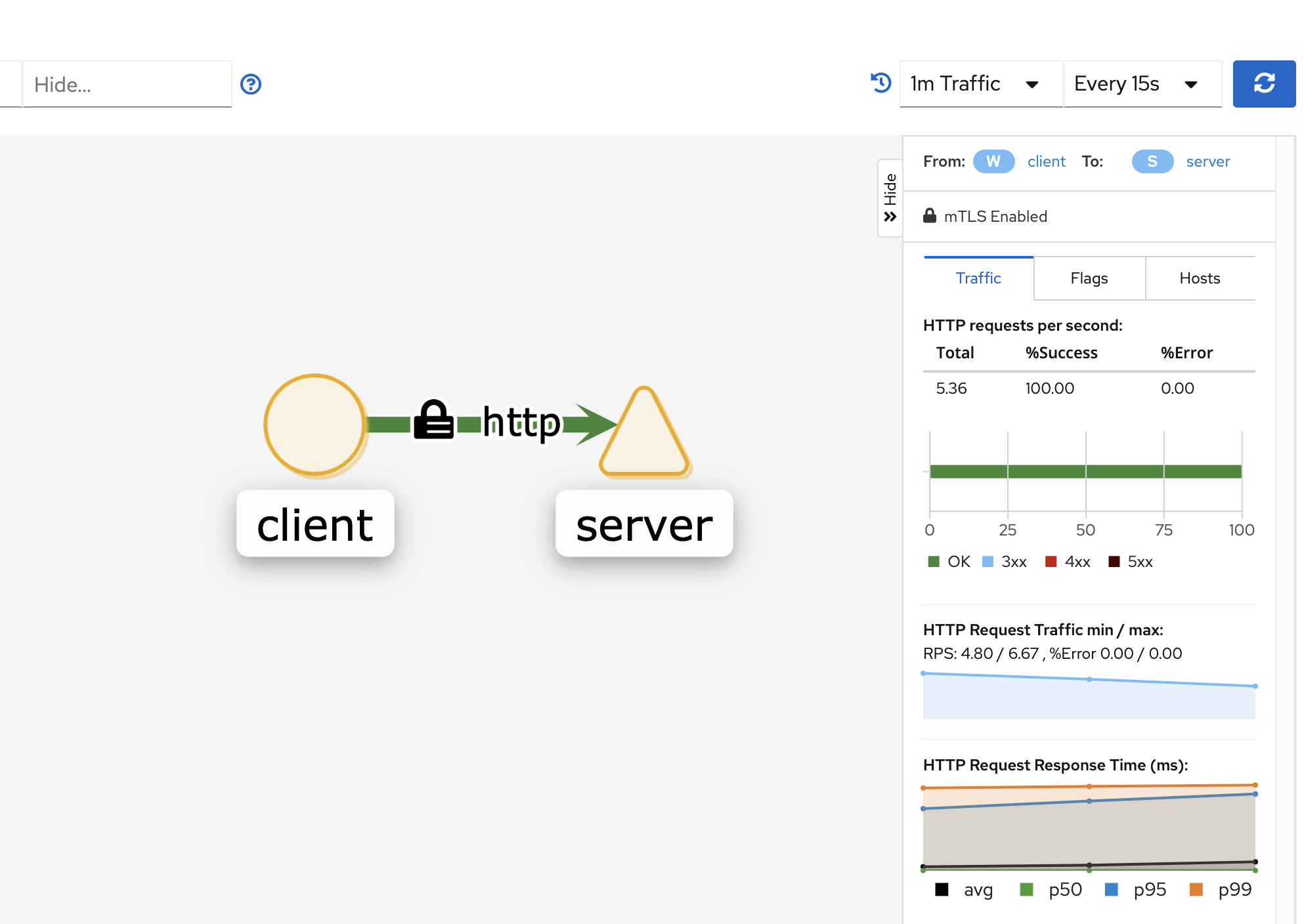
If we view the Kiali service graph for this mesh, we can see a lock icon indicating that traffic is encrypted between client and server:
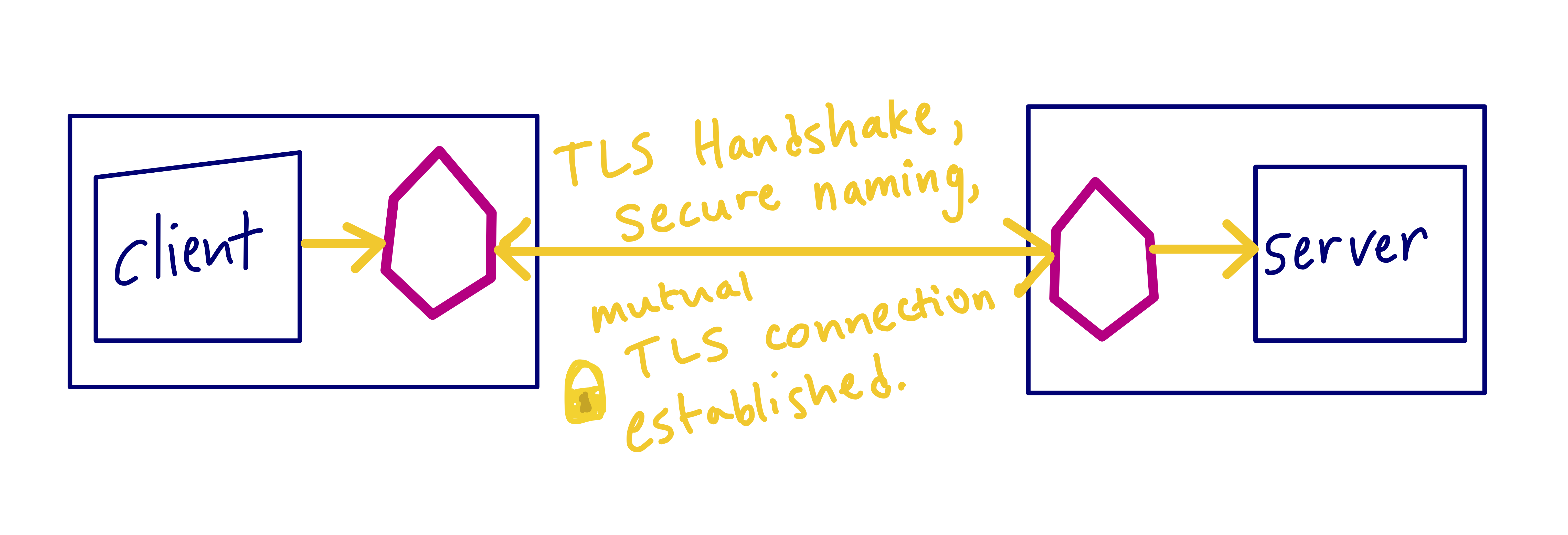
Authentication Flow:
clientapplication container sends a plain-text HTTP request toserver.clientproxy container intercepts the outbound request.clientproxy performs a TLS handshake with the server-side proxy. This handshake includes an exchange of certificates. These certs are pre-loaded into the proxy containers by Istio.clientproxy performs a secure naming check on the server’s certificate, verifying that an authorized identity is running theserver.clientandserverestablish a mutual TLS connection, and theserverproxy forwards the request to theserverapplication container.
Learn more: